Website sections
Editor's Choice:
- Guest houses for the new year
- Eye of the planet information and analytical portal
- All about Brezhnevka: panel houses
- Dacha Kichkine in Crimea: photos, how to get, reviews of tourists, hotel and sanatorium
- The most common layouts of apartments in typical houses in Russia
- Redevelopment Project Standards
- The last days of the Romanovs in Crimea
- Palace cottage alexandria
- Coordination of the demolition of the wall: what documents are needed
- Classic bedroom for men
Advertising
| Panel five-story buildings of the 80s of the series. The most common layouts of apartments in typical houses in Russia |
|
Buying new housing in a multi-storey building, people often wonder what series the building has, whether it is subject to demolition, what features it has. It is unlikely that you can answer such questions yourself, which is why we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the information in our article. Here you will find answers, facts and many useful sections to present the whole picture. House emergency and liquidationFirst of all, let's start the article with a section on houses that should be demolished in the near future, or on buildings with a minimum life span:
They are not subject to reconstruction, although many service companies “warm” good money on them, closing cracks on the walls every year. At the same time, there are a series of brick houses that can be called "unbearable", 1-511 and 1-447 belong to them. In these houses, stronger and thicker walls, increasing the thermal insulation properties of the building, the layout of apartments is also considered the most acceptable. On the other hand, no one has canceled the repair for house communications. And if in your house the owners of apartments do it yourself, this can significantly reduce the service life of building materials. Series of 5-9 floor housesIn this section, we will consider a series of brick houses that have been registered, operated and continue to be built:
A variation of the 80th seriesSeparately, we can say about the 80 series, which includes three modifications (all houses are brick):
More modern seriesIn this section, we describe several typical houses that began to be built in the last century, but continue to be built to the present (or have recently been "closed"):
Houses of two capitalsIn this section, we describe four series that can be found both in Moscow and in St. Petersburg:
What to do if the series at home is unknownIt also happens when people don’t know which series their house belongs to, but it can (when selling and buying an apartment) bring unnecessary trouble. The easiest way is to look into the technical passport, it can be taken from the management company, everything is described in detail there. There is also instruction on when they did the repair, what communications and much more. But you can also “smash your head”, define several parameters and compare them with known data. To do this, you must:
Then look on the Internet, find a special directory in which the received data is entered, and enter your information. After that, you will be given several options with photos in which you can easily find your home. Another way to find out a series of brick houses is simply to compare the appearance of the proposed options on the Internet. The likelihood of coincidence is small, since many houses look almost identical, but they have different series, so it is better to contact the house management service. OutputA series of houses is important only in cases where it is necessary to sell or buy an apartment, make repairs and check the building for breakdowns. This is not to say that we have listed all the existing series of brick buildings, but most of the exploited houses of the Soviet era are described. In the video presented in this article, you will find additional information on this topic. For political, ideological and demographic reasons, the period of the Khrushchev "thaw" was the first in the history of the Soviet planned economy, when along with the development of heavy industry, a significant increase in the production of consumer goods and everything related in one way or another to the needs of people, and the non-military industrial complex and resource-consuming raw materials, was supposed industries. The first in the USSR four-story frame-panel house was built in 1948 in Moscow on 5th St. Falcon mountains (G. Kuznetsov, B. Smirnov). Currently, his address is Prospect Budenny, 43. At this time, the country's leadership set the task for the builders to create the cheapest housing project with the possibility of family-based settlement (that is, with separate rather than communal apartments). The first step in the implementation of this task was the introduction of the idea of \u200b\u200bindustrial panel housing construction with a supporting frame. In the years 1948-1951. V. Posokhin, A. A. Mndoyants iv. P. Lagutenko was built up with a 10-storey frame-panel houses quarter in Moscow (Kuusinen, Sorge streets). In the same year, a project was developed for a frameless panel house (built since 1950 in Magnitogorsk). In 1954 in Moscow on the 6th st. The October field was built 7-storey frameless panel house (G. Kuznetsov, B. Smirnov, L. Wrangel, Z. Nesterova, N. A. Osterman). Khrushchev, the design of which was carried out since the late 1940s, went into series after a historical decree 1955 "On eliminating excesses in design and construction" ("the ostentatious side of architecture, replete with large excesses", characteristic of the Stalin era, now "does not correspond to the line of the Party and the Government in the architectural and construction business. ... Soviet architecture should be peculiar and simplicity, austerity and cost-effective forms of Solutions "). The ideological and scientific justification of the new course came down to the following points:
The turning point was the 1956 Decree “On Measures for Further Industrialization, Improving Quality and Reducing the Cost of Construction” and the 1957 “On Housing Development in the USSR”. The party’s assignment to the builders was to develop projects by the fall of 1956 that would make housing construction cheaper and affordable for workers. So the famous "Khrushchev" appeared. The aim of the project was that in 1980, every Soviet family met communism in a separate apartment. However, by the mid-1980s, only 85% of families had separate apartments: in1986 Mikhail Gorbachev pushed the deadline by 15 years, putting forward the slogan "Each Soviet family has a separate apartment by the year 2000." The prototype for the first "Khrushchev" steel block buildings (German Plattenbau ), built in Berlin and Dresden since the 1920s. The construction of residential houses "Khrushchev" lasted from 1959 to 1985. In the years 1956-1965, more than 13 thousand houses were built in the USSR, and almost all were five-story buildings. This allowed the introduction of 110 million square meters of housing annually. An appropriate production base and infrastructure was created: house-building plants, reinforced concrete factories, etc. The first house-building plants were created in 1959 in the Glavleningradstroy system, in 1962 they were organized in Moscow and other cities. In particular, during the period 1966-1970, in Leningrad, 942 thousand people received living space, with 809 thousand moving into new homes and 133 thousand gaining space in old houses. Since 1960, construction of 9-storey panel houses has been underway, since 1963 - 12-storey houses. TechnologyAmong the typical, large-panel residential buildings are most common. Prefabricated prefabricated house components Components of a prefabricated house, which are large reinforced concrete slabs that are made in factories. In the factory, precast concrete products are manufactured according to the existing GOSTs; therefore, it is assumed that their quality should differ in a positive direction from products manufactured directly at the construction site. Ready-made construction parts are delivered to the construction site, which builders can only install. As a result, labor productivity on such a building is very high. The area of \u200b\u200bthe construction site is much smaller than that required for the construction of a brick house. Such lengthy and time-consuming processes, such as installation of reinforcement or concrete, which are characteristic of monolithic housing construction, are completely excluded. This is precisely what experts see as the main advantage of panel housing construction over other types of construction. List of residential building series1940sSince 1947, the Academy of Architecture of the USSR has been developing a fully assembled large-panel dwelling. Frame-panel and frameless houses are being built:
1950sThe height of 5 floors was chosen because, according to the norms of that time, it was the highest number of floors at which it was allowed to build lift-free houses (however, sometimes houses were also built in 6 floors with a store on the ground floor). Stalinki:
Since 1957, the construction of panel houses began - the so-called "Khrushchev". People began to call them "Khrushchov" for a number of certain inconveniences:
1960s
1970sIn 1970 was adopted Unified catalog of building partson the basis of which standard designs were further developed.
1980s
At the beginning of the 1980s, in Moscow, it was developed under the guidance of architect A. G. Rochegova series of KOPE (compositional space-planning elements), designed for the construction of "buffer zones" between new buildings and protected areas of architectural monuments and areas of mass development, as well as for the "revitalization" of the existing areas. The first houses of this series were erected in 1982 near the Vorontsov park. The project provided for the possibility of building houses up to 22 floors. At the same time, standard panel houses continued to be erected in many areas of Moscow and other cities of the USSR. 1990s The ruins of the demolished Khrushchev in Moscow The territories of demolished 5-storey panel houses are built up with 17-25-storey residential buildings, mainly with new series of panel houses. Also continuing to build panel houses of the 1988-1991 series, from 1995 they began to build brick panel houses with beige polygonal carriage triangles. 2000s
Series of monolithic housesMost monolithic buildings are built according to individual projects, however, there are several series of monolithic houses:
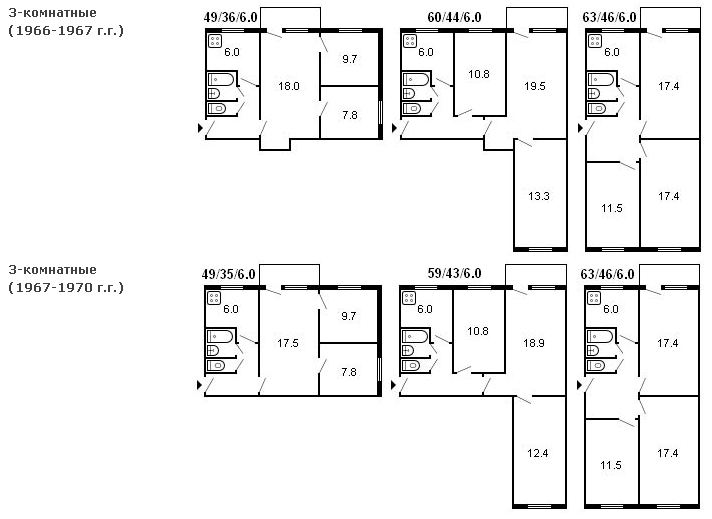
technical characteristics, quadrature scheme of a 2-room apartment series 111-121 There are several classifications of apartments. Common abbreviations and their interpretation:
Demolition of a prefabricated house
Typical apartment layouts are typical for a series of houses - a group of residential buildings that are completely or almost completely identical in design, arrangement of rooms. Also, such houses are built from the same materials. Typical layouts of apartments include "Brezhnevka", "Khrushchev", "Stalin". Houses from these series are found in almost every village in the country. Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to know how to solve your problem - contact the online consultant form on the right. It is fast and free! Stalin's houses are still expensive and prestigious. This is mainly due to their location: as a rule, the "Stalin" are located in the city center and in the areas closest to it. In addition, the large total area as well as high ceilings affect the cost of housing. "Stalin" are divided into two types, depending on the building material used: cinder blocks and brick. Most of the brick houses were built in the early period, and cinder blocks began to appear at a time when developers got access to building panels and blocks. Brick buildings usually have better thermal insulation, a more attractive facade. Cinder block houses look less elegant, and sometimes just dull. The construction of "stalinka" significantly decreased in 1956, when industrial mass housing construction began, which caused the appearance of entire arrays of "Khrushchev". The main features of the layout of "Stalin":
In "stalinkas" usually three- and four-room apartments, options with two, as well as five or more rooms are much less common. One-room apartments are completely rare. "Stalin" can refer to ordinary or nomenclature houses. Nomenclature were built specifically for elite residents. These houses have a beautiful layout, spacious hallways. In apartments, there may also be not only a children's room, but also an office, a library, a room for a servant. The kitchen in such "stalinkas" is large, the bathroom is separate. Usually located on one floor of 2-4 apartments. Ordinary houses are simpler and more modest, the area of \u200b\u200bapartments in them is less. Layouts of apartments of standard series - Stalinki:
Did you know that you can make good money by renting apartments? Read useful recommendations on rental business here Typical layout of apartments "Khrushchev"The "Khrushchev" includes five-story houses, the construction of which began in the period 1956-1964, during the reign of Khrushchev. In Moscow, these buildings were built before 1972, and in the region itself and in many other regions of the country - until the mid-1980s. At first, the Khrushchevs were built of bricks, but in the 60s, for economic reasons, panel housing began. Apartments in Khrushchev’s have a small area of \u200b\u200brooms (for example, 6-9 m2 were allocated for a bedroom), and the area of \u200b\u200bkitchens does not exceed 6 m2. The height of the ceilings also decreased - up to 2.5 meters. The main disadvantages of the layout of apartments "Khrushchev" include:
But these houses have their advantages. This is, first of all, the low cost of apartments and good territorial location - not far from the metro, in areas with developed infrastructure. Layouts of apartments of standard series - Khrushchevka:
Typical layout of apartments "Brezhnevka"Typical Brezhnevka houses were built during Brezhnev - from 1964 to the early 80s. In contrast to the "Khrushchev", such houses had a greater number of floors and an increased area of \u200b\u200bapartments. In the very first apartments, the Khrushchev refrigerator was often present, which was a closet under the kitchen window. This decision was borrowed from the "Khrushchev". The bathroom was created separate. In the future, the layout changed a little, some of the solutions are applied in our time. For "brezhnevka" characterized by an improved layout. But this is true only in relation to the "Khrushchevs", as for the "Stalin", they are more comfortable for living. In the Brezhnevka houses, the ceilings are not too high, the kitchens are small (about 7–9 m2). The number of rooms varies from 1 to 5. One of the varieties of "brezhnevka" are hotel-type apartments. They are small, their total area is 12-18 square meters. Such apartments were intended for temporary stay, but then most of them were fixed on an ongoing basis. In the "Brezhnev" houses there is an elevator, a garbage chute, and the ceiling height is 2.65 meters. Most buildings have poor thermal insulation, therefore, recently they have been undergoing major repairs in order to improve energy efficiency. Layouts of apartments of standard series - Brezhnevka:
Modern layout of apartmentsSince the mid-90s of the last century, they try to give individual buildings typical buildings. As a result of this, they cannot be attributed to a certain type of layout. During Yeltsin’s tenure, “elites” arose, but their series do not have similar features. Their construction began in connection with a change in housing standards, due to which the apartments began to have a large area, improved layout. Most houses in cities are typical brick buildings, with apartments of standard layouts. A series of houses of the Stalin type - buildings made of light-colored bricks or mineralized panels. This project stands out for its excellent layout, significant ceiling height. For external work, materials with granite chips were often used. Such houses are distinguished by towers of the "Kremlin" type. The construction of steel began in the 30s of the XX century. Similar structures were created according to individual designs, but there are many typical houses. Such structures have little resemblance to the structures of the old foundation. Khrushchev - a panel, brick or block structure. The initiator of such buildings was N. S. Khrushchev, they are completely devoid of any frills in the design and construction. They were built until 1972, inclusive, and in some areas - until 1980. Distinctive characteristics of such buildings:
After 2000, houses on 5 floors began to be demolished. The Khrushchevs in the 8th and 9th floors were not subject to demolition. The first buildings of the Khrushchev - houses of the series 1-335. They were erected in many cities of the USSR. Due to the lack of thermal insulation, such buildings are subject to demolition. Designs of a series 1-439, 1-439Я - 5-storey buildings of block type. Such a plan of buildings was built mainly in the northern regions of the USSR. Khrushchev series 1-447 - a popular type of buildings. Similar structures were built until 1970 inclusive. The height of the rooms is up to 3 meters. Panel Type BuildingsBuildings of type 1-464 are popular structures of the panel plan of the times of the USSR. They were erected in the first period of the Khrushchev building. Only from 1958 to 1964 The construction of such structures involved more than 200 house-building plants in all regions. The 1-466 series of brick houses are typical examples of residential buildings on 1,5 floors. The height of the rooms is 3 m. They were built exclusively in Moscow (its northern part). Walls of brick houses made of fragile vibro-brick. At the end, up to 6 panels are installed. Such houses are short-lived. The 1-467 series houses the first panel structure that has a pitch of load-bearing walls. For the first time, the design of such buildings included a variation in the layout of a 1.2.3-room apartment. Houses in 1-5 floors of a similar plan were built in the suburbs and other parts of the country. Houses of the 1-510 series are fairly common block 5-storey houses. Their feature is the thickness of the outer walls, which is up to 40 cm. These are durable buildings, but some of them are demolished during various reconstructions of the city’s quarters. Structures of type 1-511 - multi-sectional construction, brick Khrushchev in Moscow. In such houses apartments for 1-2-3 rooms are provided. There are several modifications of buildings that distinguish by the height of the apartments, the quality of building materials, the type of roof. Types of MG facilitiesHouses 1MG-300 or MG-300 - panel buildings in 5 floors. Their feature is the presence of square balconies, the cubic capacity of which is small. There are 3 apartments on each floor of such a house. They were built until 1968 inclusive. Buildings of the 1P-303-2 type are a 5-storey panel building, the second most frequent building in Moscow and the region. A distinctive feature of 5-storey buildings is sloping balconies, including end ones. Structures of type 11-07 are one of the first prefabricated houses of 5 floors in Moscow (its south-western part). The construction period is 1958-1961. These houses are in disrepair, most of them have already been demolished. Buildings 11-07-19 - panel buildings with fragile external walls made of vibro-brick. Often houses are tiled, each of them has 4 narrow windows at the ends. Almost all structures of this format are in disrepair, but they are only demolished in the western parts of Moscow. Houses 11-17 - modification of the series 1-510. They have increased area of \u200b\u200ba one-room apartment and a large area of \u200b\u200ba 3-room apartment. Such houses were built in the 60s. of the last century in Izmailovo, Nagatino. Small objectsThis is an example of Khrushchev’s above 5 floors in Moscow. Most of them are 8-, 9-storey block constructions. Each apartment of such a house has a sitting bath; in two-room apartments, rooms are often adjacent.
Building 11-32 is a typical panel house made of vibro-brick, the external walls of which are tiled. A characteristic feature of such buildings is balconies on pillars. A variation of this series - 11-32-130 - houses with small apartments (small families). They are intended for small families. The room has an average of 9-13 square meters. m., and the kitchen has a cubic capacity of not more than 3-3.5 square meters. m Buildings 11-34 are an example of 5-story brick structures with small families. Similar buildings were erected in the capital in different places (1-2 houses in sleeping areas). These are two-building houses, which are connected by a one-story section, in the center of which there is a room - a dining room. Buildings of type 11-35 - 5-storey brick houses with two-room and three-room apartments. Their distinctive feature is the presence of rather large external panels. Such houses were often built in 1959-1962. Today they are all demolished. Objects 11-38 and BrezhnevkaConstructions 11-38 are the first panel-type houses of volume elements. The rooms of the apartments were assembled at the factories, and at the construction sites they were only mounted. These were experimental, test structures, they were erected in 1959-1962. in Lublin, Cheryomushki. Such structures are also found in Perm, Minsk. Type K-7 - Khrushchev frame, panel type. These are massive buildings in Moscow, 1958 construction. Their walls are the thinnest among all, because their demolition is a priority. The Khrushchevs, who did not justify themselves at all, were replaced by Brezhnevka. Initially, these are 8-, 9-story buildings, which then turned into 12- and 16-story buildings. These are the first constructions with elevators and garbage chutes. The layout of apartments in such buildings has become more advanced and modern. They improved noise and heat insulation.
The layout of apartments in such houses has become more convenient. The construction of such houses began in the 70s. last century. Such houses can rightly be called the prototypes of modern buildings. After brezhnevok began to build buildings on standard designs. The most common series of modern panel buildings are KOPE, KOPE-M-SAIL, 155 and i-155m, p-3m, P-44m. |
| Read: |
|---|
New
- Rental cottages for the new year
- Modern design kitchen living room, photo ideas
- The interior of the dining room in the house
- Children's center for the little ones
- Interior studio 30 sq m
- The best design project for a studio apartment
- How to arrange indoor plants
- Small beautiful country houses
- Rent a house for the new year
- The interior of a country house - photo of wonderful design work